NASA X-Hab 2025: Modular Robotic Construction
This is a stub. You can help by expanding it.
Overview

In 2024, NASA's M2M X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge for 2025 was released, for which the Aurora Robotics Lab at the University of Alaska Fairbanks was accepted and funded through NASA’s 2024–2025 Moon to Mars X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. Our goal was to explore modular robotic construction techniques for lunar infrastructure, especially focusing on micrometeoroid-resistant arch structures made from modular steel trusses and covered in lunar regolith, with a clear path to fully autonomous robotic construction.
The project culminated in the development of the Excahauler robotic platform with a custom-built arm and end-effector, capable of aligning and assembling scaled modular truss components. Despite limitations in time and resources, the team demonstrated capabilities including truss manipulation, partial structural testing, and scale backfilling with regolith simulant (snow).
This wiki page is a very abridged version of our full final report which should soon be added to NASA's NTRS database.
Project Vision and Mission
- Long-Term Vision: Transform the solar system using robotic construction with local materials.
- Short-Term Vision: Develop robotic infrastructure construction technologies for the Artemis Base Camp.
- Mission: Design and demonstrate robotic tools and modular structures capable of assembling scalable micrometeoroid-resistant lunar shelters.
The L-Truss System

The primary structural innovation was the development of the L-Truss: A modular trapezoidal truss segment. These trusses connect via push-fit endplates and spring-loaded capture pins to form straight or curved assemblies, including arches and retaining walls. The final full-steel design used plasma-cut end plates with a 3D printed door latch-style connection. However, full robotic connection could not be demonstrated with this design, so we made some last minute changes. The final prototype design included:
- Hybrid steel construction with 3D printed carbon-fiber polycarbonate alignment funnels.
- Spring-loaded pin latching mechanisms for tool-free robotic assembly.
- Optional upright members for regolith support and buckling resistance.
- Final tested form: 1.5m long, ~3kg, with a base angle of 22.5°.
A scale 3D printable version is publicly available: L-Truss Model
Structure Requirements
- Accommodate 2.6m x 2.6m vehicles within the constructed arch structure. (I.0)
- Truss segments must remain under 2.0 meters for transport and robotic handling. (I.1.1)
- Regolith shielding: Support ≥0.2m regolith equivalent for radiation/thermal protection. (O.0)
- Minimum compressive load capacity of 300 kgf with ≥2.0 safety factor. (I.1.2, I.2.1)
- Robot-compatible assembly path: all actions must have potential for automation. (E.0, E.2)
Concept of Operations
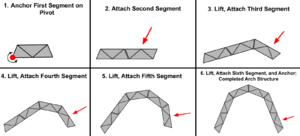
Lunar Deployment Plan
- Site Preparation: The Excahauler prepares a foundation using excavation tools.
- Truss Deployment: Trusses are unloaded from a logistics lander and staged for assembly.
- Structural Assembly: Robots assemble the arch structure according to the graphic on the right.
- Backfilling: Lunar regolith is put over the structure via ballistic throwing or traditional scooping.
- Use Phase: Covered arches serve as shielding for sensitive lunar equipment or crew.
Ground Demonstration Activities
- 1:10 scale arch model tested with regolith simulant (basalt dust).
- Full-scale hybrid trusses fabricated and manipulated via teleoperation.
- Robotic assembly verified using Excahauler and custom-built 2500:1 reducer gearbox arm.
Project Phases
- System Definition Review (SDR): October 4, 2024
- Preliminary Design Review (PDR): November 15, 2024
- Critical Design Review (CDR): January 24, 2025
- Progress Checkpoint Review (PCR): April 18, 2025
- Final Report: May 23, 2025
Robot System: Excahauler
- Originally designed for the 2022 NASA Break the Ice Challenge.
- Outfitted with a custom modular manipulator arm with 3D printed stepped planetary gearboxes.
- Used in successful teleoperated tests to transport and align L-Truss segments.
Software and Simulation
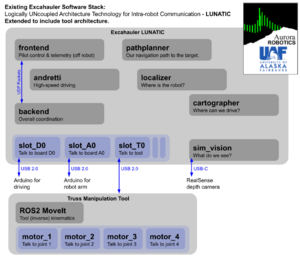
The team developed and tested robotic workflows using the following tools:
- Godot-based simulator: Visualized structure assembly and layout.
- Custom autonomy stack (LUNATIC): Handles teleoperation, control, and vision.
- ROS2 / MoveIt: Inverse kinematics modeled, full integration for automation incomplete.
Testing and Validation
- FEM analysis showed safety factor >2.6 under 500N compressive loads.
- Hybrid trusses withstood >500N axial loads; failure occurred at 230N in bending.
- 1/10 scale arch supported >12kg in Earth gravity, equivalent to 36+ tonnes in Mars gravity at full scale.
Educational Integration
Project integrated into UAF's CS 493 (Fall) and CS 454 (Spring), providing hands-on systems engineering experience to undergraduates and graduate students in mechanical and computer science disciplines.
Outreach Activities
- UAF Party in the Park: Public engagement event with live robot demos.
- FTC Robotics Tours: Guided tour for K–12 robotics students.
- UAF Engineering Open House: Structural demo and recruiting opportunity.
Lessons Learned
We were not able to complete our promised deliverables to full satisfaction due to time constraints and lack of defined leadership structure. We learned important lessons about:
- Structure: Even small teams benefit from defined leadership and task ownership.
- Planning: Conservative scoping ensures project deliverables can be met.
- Fabrication: Early design-for-manufacturing saves time and enables iteration.
Future Work
- Complete full-scale robotic arch assembly.
- Fully integrate MoveIt into robotic control stack for autonomous alignment.
- Refine end-effector precision and truss fabrication for large-scale repeatability.
Additional Information
- Project Lead: Andrew Mattson, UAF CS BS/MS student
- Faculty Advisor: Dr. Orion Lawlor (oslawlor@alaska.edu)
- Team Members:
- Elliott Madsen (ME BS)
- Delano Horner (ME BS)
- Daniel Schliesing (ME BS)
- Kory Lamme (ME BS)
